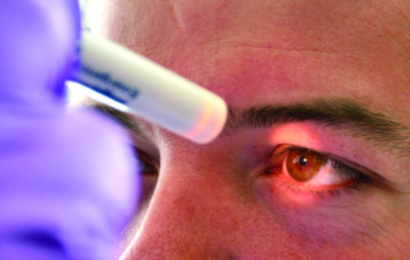
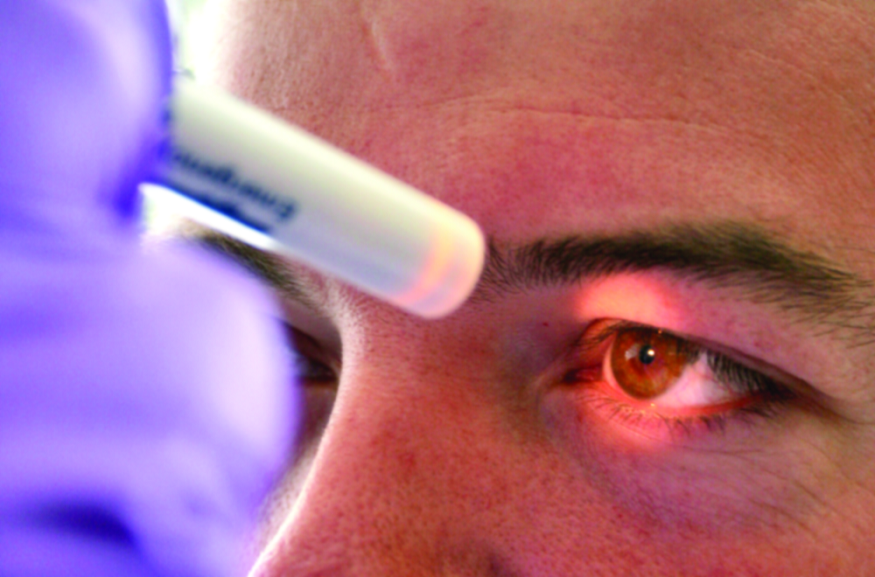
The human eye appears as a simple organ in the eyes of a naïve person, but biologically and medically it is much more complicated than it appears to be. The human eye and pupil are closely connected to the external and internal factors of the human body. These environmental and internal factors can affect the pupillary size measurement. The pupil regulates the amount of light that enters our eyes; it contracts in bright light and it dilates in the dark. We will discuss every internal and environmental element that may have an impact on pupil size in this blog.
Internal Factors Impacting Pupil Size
Traumatic Brain Injury
TBI can impact pupil size and with the help of additional neurological tools critical care doctors measure pupil size for critical patients. The changes in pupil size due to TBI denote the internal neurological conditions and physicians assess the neurological function with the use of NPi, a standardized measurement of pupil reactivity.
Autonomic Nervous System
The two branches of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, are responsible for regulating pupil size. Pupil dilation, or mydriasis, is a condition caused by the sympathetic nervous system, which is frequently linked to the body’s “fight or flight” response. This condition improves eyesight in low-light or stressful environments. The modern-day pupilometer can detect the slightest alteration in pupil size.
Emotional State
Many people may find it weird if we say that our emotional state impacts our physical body. The thing is we fail to notice all the subtle changes. Emotional changes can impact pupil size significantly. A sudden surge of happiness or arousal can dilate the pupil. Fear or any kind of negative emotion can constrict the pupil.
The Age Factor
The impact of age on pupils is irreversible. With age, our pupils generally become smaller known as senile miosis. Smaller pupils are a typical aspect of aging and can impair eyesight in older persons, especially in low light.
Medications and Substances
A range of medications and substances can have an impact on pupil size. Amphetamines and several antidepressants, for instance, stimulate the sympathetic nervous system and can produce pupil dilation. However, several antipsychotic drugs and opioids can cause narrowing of the pupils.
External Factors Affecting Pupil Size
Light Exposure
Light can be considered as the most immediate external factor influencing pupil size. In bright light, pupils constrict to protect the retina from overexposure to light and to enhance near-object focus. Pupils dilate in low light to let more light into the eye, improving vision in low light.
Visual Focus
If you focus on an object from different distances your pupil size can change. If we go for a traditional eye test, this process often helps doctors determine lens power.
Cognitive Load
Undertaking intellectually taxing activities may cause alteration in pupil size. Studies have indicated that when students are required to put in a lot of mental work, like when solving complicated puzzles or focusing intently, their pupils dilate.
Interplay Between Internal and External Factors
There are many situations when there is interplay between the internal and external factors that impact the pupillary size measurement.
Health Implications
Pupil size variations can demonstrate important details about an individual’s health. For example, anomalous pupillary responses may indicate the presence of neurological conditions like Adie’s pupil or Horner’s syndrome.
Clinical Applications
In clinical applications, pupil size and reactivity are often evaluated as part of a neuro exam. These assessments can help diagnose stroke, brain injuries, or the effects of medications.
Numerous internal and environmental factors, such as light exposure, cognitive load, emotional states, and autonomic nervous system activity, can affect the size of the pupil. To control the amount of light entering the eye and improve vision in different situations, these variables interact in intricate ways. Understanding of the mechanisms underlying these pupil size alteration can be extremely beneficial for clinical applications and offers insightful knowledge of human physiology.
We can gain a deeper understanding of the complex workings of the human visual system and how it relates to general health and well-being by identifying the various factors that affect pupil size.